SpaceX makes history
February 7, 2018 | Expert Insights
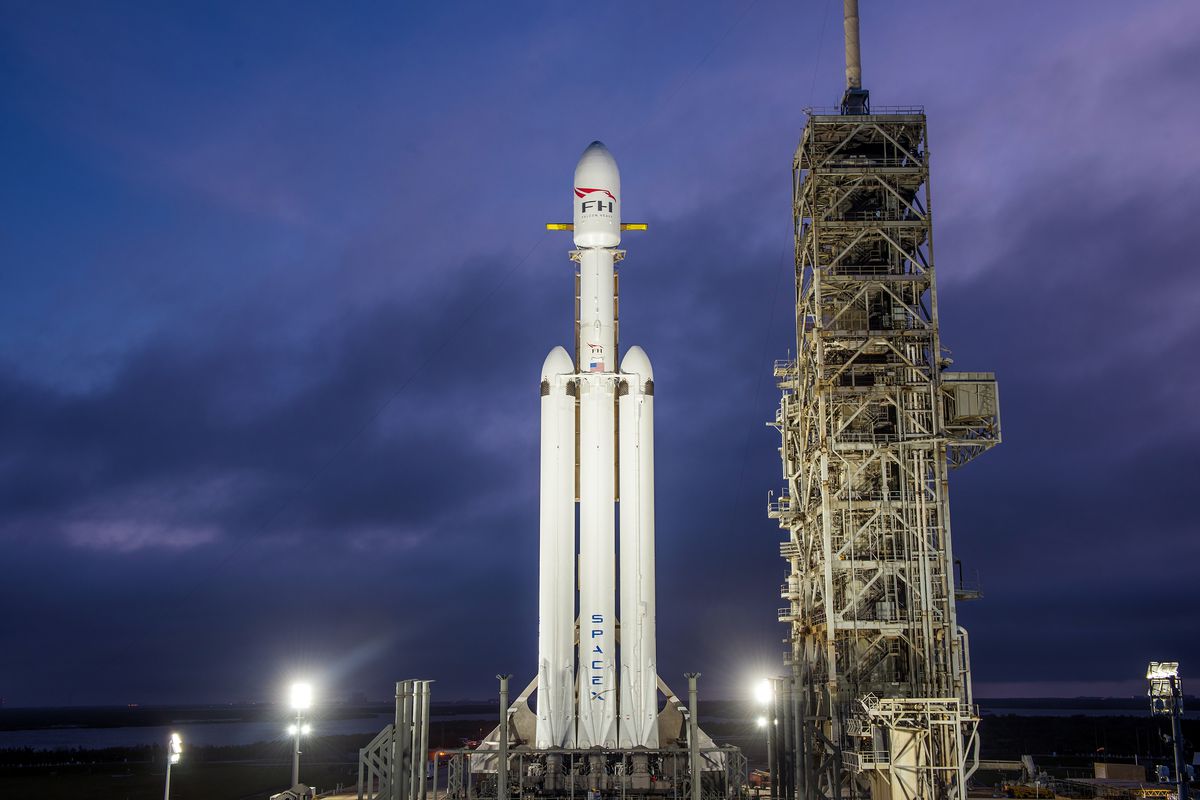

Conceptualised 7 years ago, Falcon Heavy is a reusable super heavy-lift launch vehicle designed and manufactured by SpaceX. Falcon Heavy is the cheapest satellite for its capabilities to date. The rocket was launched at 3:45 pm local time on the 6th of February from the Kennedy Space Centre. At $90 million per launch, it is capable of carrying double that of the second most powerful rocket in the world, at one third the cost.
Background
Elon Musk is a South African-born Canadian American business magnate, investor and inventor. He is best known as the founder, CEO and CTO of SpaceX. SpaceX is a private American aerospace manufacturer and space transport services company founded by Musk in 2002. Musk is known for his aspiration to enable both the colonisation of Mars, and reduce costs of space travel within the next two decades.
SpaceX has since developed the Falcon launch vehicle family and the Dragon spacecraft family, which both currently deliver payloads into Earth’s orbit. SpaceX’s achievements include the first privately funded liquid-propellant rocket to reach orbit (Falcon 1 in 2008). It was also the first privately funded company to successfully launch, orbit, and recover a spacecraft, called “Dragon”.
There are currently two space stations capable of human occupancy in orbit. The first is China’s Tiangon-2 space laboratory, which has been manned at longest for a month. Crews to this station are transported using the Chinese Long March launch vehicle.
The second is NASA’s International Space Station, which recently celebrated the 20th anniversary of the Intergovernmental Agreement that enabled its conception. The ISS houses 6 astronauts at any given point; three of these astronauts are expected to land in February, and another 3 scientists will launch for the station in February in NASA’s Expedition 55. The astronauts are transported by the Russian Soyuz program that uses Soyuz launch vehicles.
In 2014, SpaceX signed a 20-year agreement with NASA for the use and operation of their Kennedy Space Centre launch pad. The first ever spacecraft sent to the International Space Station (ISS) by a private company was also achieved by SpaceX. As of March 2017, the company has flown 10 missions to the ISS under a cargo resupply contract, and conducted 18 orbital launches in total.
Analysis
Falcon Heavy is also known as the most powerful rocket in operation and is capable of carrying 64 tonnes to a low-orbit recipient more payload than any other US-made rocket since NASA’s (now retired) Saturn V rocket used for the moon landings in 1969. Musk has said that the company could do another Falcon Heavy flight as soon as six months from now, this time with a commercial payload.
The rocket was launched at 3:45 pm local time from the Kennedy Space Centre. The side boosters detached and landed safely, after the Falcon reached the upper layers of the Earth’s atmosphere, however the third missed its mark to crash into the Atlantic. The recovery and reuse of the boosters is what cuts expenses heavily.
The rocket is intended to eventually be in elliptical orbit around the sun and between Earth & Mars.
As a part of the rocket’s test payload was Musk’s old red Tesla roadster, with a mannequin nicknamed “Starman” in the driver’s seat. On the radio system, Bowie’s “Space Oddity” plays on repeat, on its circuit board is printed the phrase, “made on earth by humans”. The car is meant to be launched into orbit around Mars, and stay there for approximately 6 months. Musk has put up four and a half hour livestream of the car on his twitter.
As covered earlier, Musk expressed doubts about the project prior to the launch. “Falcon Heavy required the simultaneous ignition of 27 orbital-class engines. There’s a lot that could go wrong there,” he said at a conference last year. “This is one of those things that’s very difficult to test on the ground… Real good chance that the vehicle does not make it to orbit.”
Lately, development in space travel has largely had a scientific purpose, such as NASA’s well known Mars rover “Curiosity”, probe to Saturn “Cassini”, and “Juno”, the spacecraft currently monitoring Jupiter. While the Falcon Heavy will provide much assistance to scientific endeavours as well- larger, more capable equipment, robots, and telescopes- it could also serve multiple other purposes. This includes larger and more powerful satellites- both for communication and intelligence purposes.
“The successful launch of a new vehicle on its first flight is a significant accomplishment they can be very proud of”, said current Nasa Administrator Robert Lightfoot.
Assessment
Our assessment is that if completely successful, the Falcon Heavy symbolises a step forward for human ventures into space and would have a diversity of ramifications. The capability of the rocket to carry such large loads at comparatively low costs could be critical to both current scientific endeavours as well as the possibility of future civilian travel to space- and Musk’s famed Mars mission. We believe that this mission is an evidence of the significant expansion of the commercial space flight.







Comments