India's Blockchain Leap
March 16, 2024 | Expert Insights

India, while maintaining a cautious stance on cryptocurrencies, is actively exploring the potential of blockchain technology, the underlying infrastructure that powers them. A significant development is the collaboration between the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) and the Indian Institute of Science (IISc). This partnership aims to research emerging technologies like blockchain and Artificial Intelligence (AI). The focus lies on developing scalable blockchain platforms and a multi-modal analytics platform to analyse fintech data. This initiative underscores the NPCI's commitment to fostering innovation in the payments landscape through technological advancements.
Background
In 2022, the NPCI launched Falcon, an open-source project aimed at simplifying blockchain management and use. This initiative demonstrates a commitment to fostering a collaborative and accessible environment for blockchain development. By making blockchain technology more user-friendly and readily available, Falcon can empower a wider range of stakeholders to participate in the exploration and implementation of blockchain solutions.
Furthermore, the NPCI established Vajra in the same year. Vajra is a blockchain-based system specifically designed to automate payment clearing and settlement processes for NPCI products. This real-world application highlights the NPCI's focus on utilizing blockchain technology to address practical challenges within the Indian financial landscape. By automating these processes, Vajra has the potential to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and potentially reduce costs associated with payment processing.
These NPCI-led initiatives are not isolated efforts. The government of Telangana's agreements to promote discussions around blockchain technology further underscore India's commitment to exploring this emerging field. These discussions can play a crucial role in raising awareness, fostering collaboration, and identifying potential use cases for blockchain across various sectors.
Similarly, the establishment of a dedicated impact lab focused on blockchain research and development at the Hyderabad campus of the Indian School of Business (ISB) signifies a growing academic interest in technology. This lab can serve as a hub for innovation, attracting researchers and entrepreneurs to develop and test novel blockchain applications.
Analysis
The Indian blockchain market is experiencing a period of significant activity, marked by a growing interest from both established enterprises and innovative startups. While a report by NASSCOM acknowledges that widespread adoption is still in its early stages, several trends indicate a promising future for this transformative technology.
According to NASSCOM's 2019 Report stated that a majority of mid and large service providers in India have less than 5% of their projects involving blockchain. This is significantly lower compared to projects undertaken in North America and Europe. However, this data point highlights the nascent stage of adoption and the immense potential for growth in the Indian market.
Despite the early stage, a significant number of enterprises are actively integrating blockchain. A 2023 joint report by Assocham and EY revealed that over 40% of surveyed Indian businesses across various sectors are planning or piloting blockchain projects. This upsurge in interest indicates a growing awareness of the potential benefits blockchain offers.
Furthermore, the emergence of new startups dedicated to blockchain solutions is another indicator of the burgeoning Indian market. As per a 2022 report by Inc42, over 150 blockchain startups have been established in India in the past five years. This entrepreneurial spirit is crucial for propelling the development of a robust blockchain ecosystem in India.
Interestingly, the initial wave of adoption appears to be concentrated within the banking, financial services, and insurance (BFSI) sector. A 2023 study by Deloitte revealed that nearly 70% of BFSI institutions in India are actively exploring or implementing blockchain solutions. Financial institutions are well-positioned to leverage the inherent security and immutability of blockchain to streamline processes, reduce fraud, and enhance overall transparency. By implementing blockchain solutions, the BFSI sector can potentially improve customer experience, reduce costs associated with manual processes (estimated at $18 billion annually according to a 2020 McKinsey report), and drive greater financial inclusion within the Indian economy.
Beyond the private sector, the public sector is also recognizing the potential of blockchain technology. Government agencies are exploring its use cases in areas critical to national infrastructure and citizen services. Potential applications include land title registry, which can benefit from the tamper-proof nature of blockchain to secure and transparently record ownership data. According to a 2021 World Bank report, an estimated 12% of landholdings in India lack proper documentation, leading to disputes and hindering economic development. Blockchain can play a crucial role in addressing this challenge.
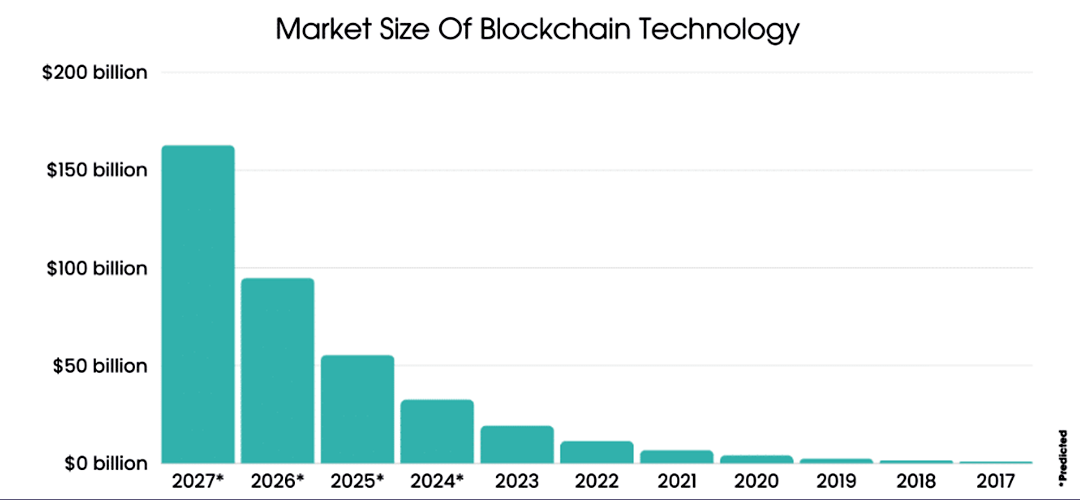
The combined efforts of the private and public sectors, coupled with the dynamism of the startup ecosystem, paint a promising picture for the future of India's blockchain market. As adoption continues to grow and the technology matures, India has the potential to emerge as a global leader in developing and implementing innovative blockchain solutions that address critical challenges and unlock new avenues for economic growth, potentially reaching a market size of $39.7 billion by 2025 as estimated by a 2020 Grand View Research report.
While India's approach to blockchain technology is marked by cautious optimism, recent developments suggest a proactive approach toward exploring its potential. The current regulatory framework remains undefined, reflecting the government's desire for a measured evaluation. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI), for instance, has expressed concerns surrounding cryptocurrencies but acknowledges the distinct value proposition of blockchain technology itself. As the technology matures and its applications become clearer, a more comprehensive regulatory framework is likely to emerge.
India possesses a significant advantage in its existing digital infrastructure. Aadhaar, a unique identification system for residents, UPI (Unified Payments Interface) facilitating real-time interbank transactions, and Digilocker, a platform for secure digital document storage, form a robust foundation for wider blockchain adoption. This infrastructure can seamlessly integrate with blockchain solutions, fostering innovation across various sectors.
One of the most promising benefits of blockchain lies in its potential to revolutionize governance. By leveraging its core principles of transparency and immutability, blockchain can enhance accountability within government institutions. Streamlined processes, coupled with readily verifiable data trails, can significantly reduce corruption and bureaucratic inefficiencies. Additionally, blockchain can empower citizens by fostering a more transparent and decentralized decision-making process.
The business domain stands to gain considerably from blockchain adoption as well. The technology facilitates "self-regulation," enabling businesses to operate with greater autonomy and reduced reliance on cumbersome regulatory oversight. This can translate to faster turnaround times and lower administrative costs. Furthermore, by providing a secure and transparent platform for transactions, blockchain empowers citizens by fostering trust in the business environment. Imagine a scenario where a farmer can track the movement of their produce from farm to market in real time, ensuring fair pricing and eliminating the need for intermediaries.
However, challenges remain on the path to widespread adoption. A key hurdle is the lack of awareness and understanding surrounding blockchain technology. Many perceive it as a potential replacement for existing systems, leading to confusion and apprehension. To overcome this challenge, India must prioritize initiatives focused on educating the public and private sectors alike. Capacity-building programs can equip individuals and organizations with the knowledge and skills necessary to harness the power of blockchain effectively.
Assessment
- By combining the efforts of government institutions, research bodies, and the private sector, India is creating a robust ecosystem for exploring and harnessing the potential of blockchain technology. This collaborative approach positions India to be a frontrunner in developing and implementing innovative blockchain solutions that can address challenges and unlock new opportunities across various industries.
- Despite these challenges, India's future in the blockchain landscape appears bright. The government's supportive stance on research and development, evidenced by collaborations like the NPCI-IISc partnership, fosters a culture of innovation. Additionally, the increasing investments from the private sector showcase growing confidence in the technology's potential.
- As the regulatory framework evolves and public awareness increases, India has the potential to become a global leader in leveraging blockchain technology. This can translate into a more secure, transparent, and efficient ecosystem across various sectors, unlocking new avenues for economic growth and social progress








Comments