Maharashtra: the Sweet smell of success
May 6, 2019 | Expert Insights
Maharashtra is arguably India's most prosperous state with the highest per capita income and strong performances in key HDI indicators. So, what is a threat to the state? Natural phenomenon arising from climate change as well as unsustainable industrial practices are Maharashtra's biggest concerns so far.
Background
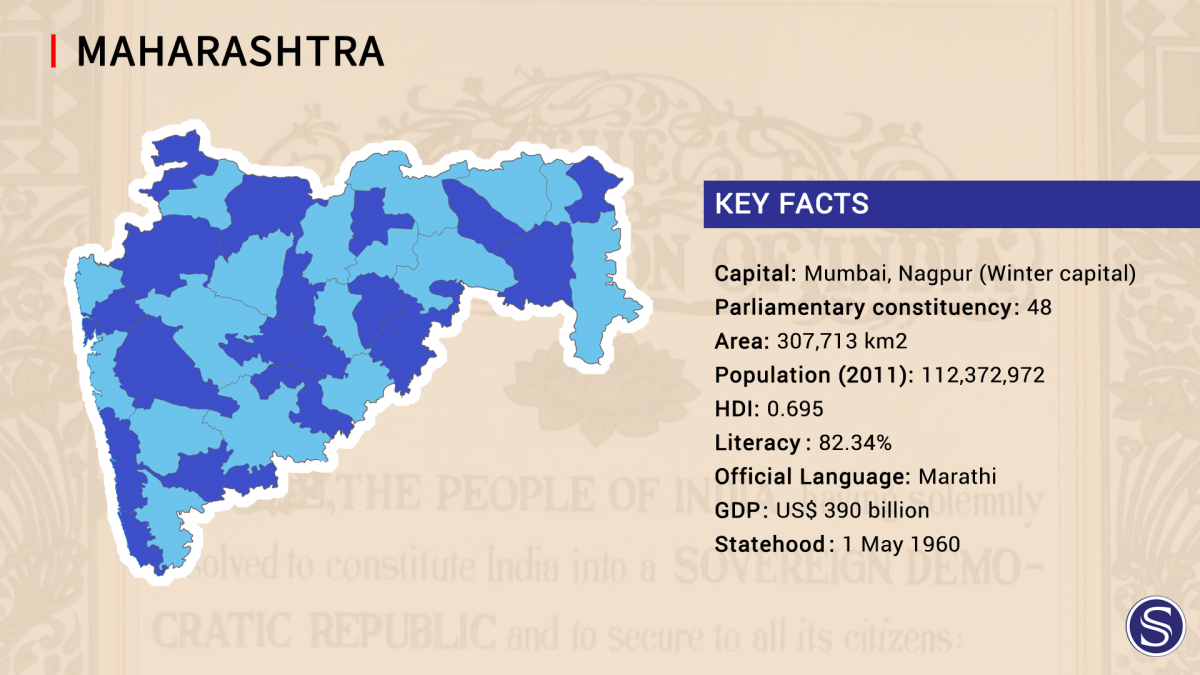
- It is the second-most populous state and third-largest state by area in India.
- It is the wealthiest state by all major economic parameters and also the most industrialized state in India. The state continues to be the single largest contributor to the national economy with a share of 15% in the country's gross domestic product (GDP).
- Maharashtra accounts for 17% of the industrial output of the country and 16% of the country's service sector output.
- The economy of Maharashtra is the largest state economy in India with ₹27.96 lakh crore (US$400 billion) in GDP and a per capita GDP of ₹180,000 (US$2,600).
- It has over 112 million inhabitants and its capital, Mumbai, has a population around 18 million making it the most populous urban area in India.
- Maharashtra was the largest power generating state in India, with an installed electricity generation capacity of 26,838 MW, using thermal power plants.
Analysis
After India's independence, the Deccan States, including Kolhapur were integrated into Bombay State, which was created from the former Bombay Presidency in 1950. In 1956, the States Reorganisation Act reorganised the Indian states along linguistic lines, and Bombay Presidency State was enlarged by the addition of the predominantly Marathi-speaking regions of Marathwada (Aurangabad Division) from erstwhile Hyderabad state and Vidarbha region from the Central Provinces and Berar.
The Mahagujarat Movement was started, seeking a separate Gujarat state. Keshavrao Jedhe, S.M. Joshi, Shripad Amrit Dange, Pralhad Keshav Atre and Gopalrao Khedkar fought for a separate state of Maharashtra with Mumbai as its capital under the banner of Samyukta Maharashtra Movement. On 1 May 1960, following mass protests and 105 deaths, the separate Marathi-speaking state was formed by dividing earlier Bombay State into the new states of Maharashtra and Gujarat. The state continues to have a dispute with Karnataka regarding the region of Belgaum and Karwar.
1) Environment: Maharashtra occupies the western and central part of the country and has a long coastline stretching 720 kilometres along the Arabian Sea. Maharashtra has a typical monsoon climate, with hot, rainy and cold weather seasons. However, dew, frost and hail also occur sometimes, depending upon the seasonal weather. The winter in January and February is followed by summer between March and May and the monsoon season between June and September. Summers are extreme with March, April and May as the hottest months. During April and May thunderstorms are common all over the state. Temperature varies between 22 °C and 43 °C during this season. Climate change is a major threat to the state as Mumbai is bound to be affected by rising sea levels. In addition, criticism has bee levelled against the downsizing of national park areas for commercial development industrialization.
2) Energy: With the second largest population of the country, Maharashtra has been able to reduce its per capita energy consumption to sustainable levels. However, the sheer volume of electricity generated and the pollution arising from that is a massive source of greenhouse gasses. Maharashtra should leverage its wealth, industrial base and skilled workforce to establish green sources of energy generation. The low-level models, if successful, could be scaled up and even emulated by other states like Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
Assessment
Our assessment is that Maharashtra has achieved phenomenal economic, social and technical success and its primary concerns are largely related to climate change and renewable energy. We believe that the state is growing are a rapid pace and this is the perfect time to focus on deploying sustainable construction methods, efficient energy grids and eco-friendly sources of energy generation to mitigate the impact of climate change-induced natural calamities.


