More hikes in US interest rates?
February 28, 2018 | Expert Insights

The new Chairman of the Federal Reserve has stated the interest rates will be further raised in the near future. He also assured to policy makers that the US economy is robust and interest rates will be raised according to the performance of the economy.
Background
The Federal Reserve System (also known as the Federal Reserve or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States. It was created on December 23, 1913. The main goal behind establishing the body was to create a central control of the monetary system that will prevent financial crises. In the event of a financial downturn, the Federal Reserve steps in to provide key aid.
Over the years, the Federal Reserve a played a key role in saving the American economy (and in turn the global economy) from imploding. It’s roles and responsibilities were expanded after the Great Depression, that caused a global meltdown. The timing of the Great Depression varied across nations; in most countries it started in 1929 and lasted until 1941. It resulted in international trade being reduced by 50% and unemployment rose.
A rise in the Fed funds rate will likely cause a ripple effect on the borrowing costs for consumers and businesses that want to access credit based on the U.S. dollar. Whenever the Federal Reserve increases the interest rates, the prime rate increases, and the credit card rates also increases among others. A hike in interest rates increases the borrowing costs for the U.S. government and fuel an increase in the national debt.
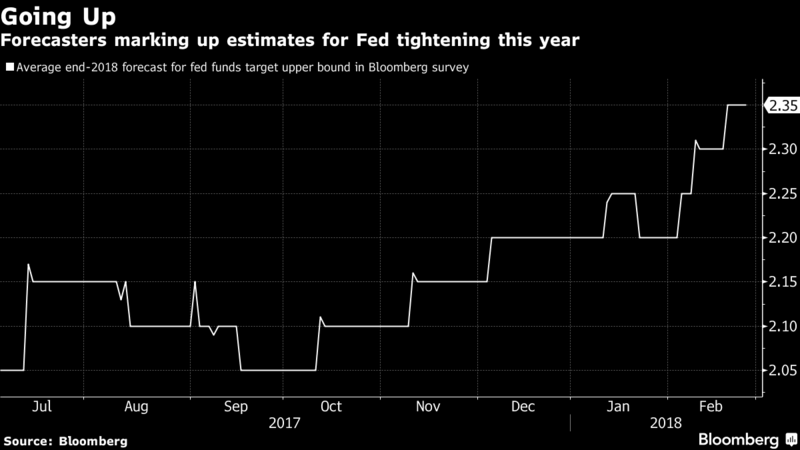
In June 2017, the Federal Reserve stated that it would be hiking key interest rates by 0.25%. This was the second time in the year when the interest rates were hiked. The hike in the interest rates were reflective of the central bank's confidence in the US economy. After a two-day meeting on 14th June, the Federal Reserve’s Open Market Committee raised its benchmark interest rate by 25 basis points from a range of 1% to 1.25%.
In December 2017, for the third time in the year, the US Federal Reserve raised the interest rates by 0.25%. The central bank has noted that this has been introduced as the US economy made “solid gains.”
The US economy expanded at an annual pace of 3% during the three months to the end of September. The growth rate is higher than what had been forecasted by experts. In the previous quarter the US GDP grew at an annual pace of 3.1%. On a year-on-year basis, GDP was up 2.3% according to estimates. The economy has grown for eight straight years, one of the longest stretches in history. Unemployment is down to 4.2%, its lowest since 2001.
Analysis
On January 2017, with a vote of 84-13 in favor Jerome Powell was confirmed by US lawmakers. When he was nominated, Powell praised his predecessors, Janet Yellen and Ben Bernanke. He said that he was “committed to making the best decisions based on the best available evidence in the longstanding tradition of monetary independence”.
In his first public appearance since becoming the new Chairman of Federal Reserve, Powell stated that the interest rates will be further hiked in the near future. He also noted that he work to ensure the economy does not become overheated.
“My personal outlook for the economy has strengthened since December. We’ve seen continuing strength in the labor market,” Powell told the House Financial Services Committee in his first hearing as Fed chief. “We’ve seen some data that will in my case add some confidence to my view that inflation is moving up to target. We’ve also seen continued strength around the globe, and we’ve seen fiscal policy become more stimulative.”
He added, “The [Federal Open Market Committee] will continue to strike a balance between avoiding an overheating economy and bringing ... price inflation to 2 percent on a sustained basis. Some of the headwinds the U.S. economy faced in previous years have turned into tailwinds. He also noted that “inflation remains below our 2 percent longer-run objective. In the (FOMC‘s) view, further gradual rate increases in the federal funds rate will best promote attainment of both of our objectives.”
Experts have stated that Powell’s testimony is also an indirect invitation to policy makers to revise their growth forecasts for the American economy. “It was very, very clear signal that they are going to do a little bit more hiking this year than was in their dots in December,” said Seth Carpenter, a former senior Fed adviser who is now chief U.S. economist at UBS Securities. “The committee is going to have to come up with a credible argument that refutes the logic he laid out” for stronger growth and possibly a faster pace of tightening.”
In the event that the economy does overheat Powell said that, “we’ll have to raise rates faster, and that raises the chances of a recession, and recessions tend to hit vulnerable populations the most. We’re trying to balance the risk of getting inflation up to 2 percent with the risk of the economy overheating."
Assessment
Our assessment is that the strong economic growth along with a drop in the unemployment rate in the US has provided confidence to investors and equity markets have risen as a result. As the interest rates are hiked, there are implications for emerging economies like India. There could result in a reduced inflow of FII investments into Indian markets and could also put some pressure on the value of rupee.







Comments