Monetary Policy of Bitcoin
January 21, 2022 | Expert Insights

Bitcoin was created as an alternative to central banks. In the current banking system, central authorities make decisions that impact the entire economy. Bitcoin was a response to the 2008 financial crisis, where the role of central banks in fomenting the crisis had come under increasing scrutiny. In this context, it becomes critical to understand how monetary policy will be shaped in the age of crypto.
Background
In the current system, the supply of money is controlled by a central authority, in most cases a central bank. The central bank can manage the economy by using monetary policy tools, and its ultimate goal is to make sure that the economy is growing at a stable pace. They can use these tools to promote growth during periods of recession or to slow down growth during periods of inflation.
The central bank uses four main monetary policy tools: reserve requirement, open market operations, discount rate and interest on reserves. These tools work by increasing or decreasing the total liquidity in an economy, which directly impacts the total money available to invest, lend and spend. They also use other tools to regulate the economy. In the U.S., for instance, the Fed employs tools like direct lending to businesses, supporting money market funds, supporting credit card markets and commercial papers.
Analysis
When the Indian government was pushing for a total crypto ban, one of its major concerns was that the decentralised nature would threaten the country's macroeconomic stability. There was no way to ensure that a monetary policy could be enforced in relation to these currencies.
To some extent, crypto has similar properties to government-issued currencies, such as: serving as a medium of exchange, a store of value and a unit of account. Currently, due to the highly speculative nature of crypto, it has not yet reached the stability required to act as a currency. However, if the growth of crypto becomes slower and more stable and continues to increase in value, it could be the alternative to central bank currencies.
Bitcoin supporters believe that its algorithm will better counter inflation than any central authority and help people save the value of their money. In a world where there is currency competition, people are more likely to favour the currencies that give them a higher return and act as a hedge against inflation.
In theory, bitcoin is seen as a hedge against inflation (like gold) due to its value being created by speculation and its limited supply. In a free-market economic system, prices are supposed to reflect the knowledge and act as a coordinating force for economic production. Hence, the value of bitcoin represents the most efficient allocation of money. The issue with a centrally controlled monetary system is that it cannot have the same knowledge as the entire market and hence can never be as efficient.
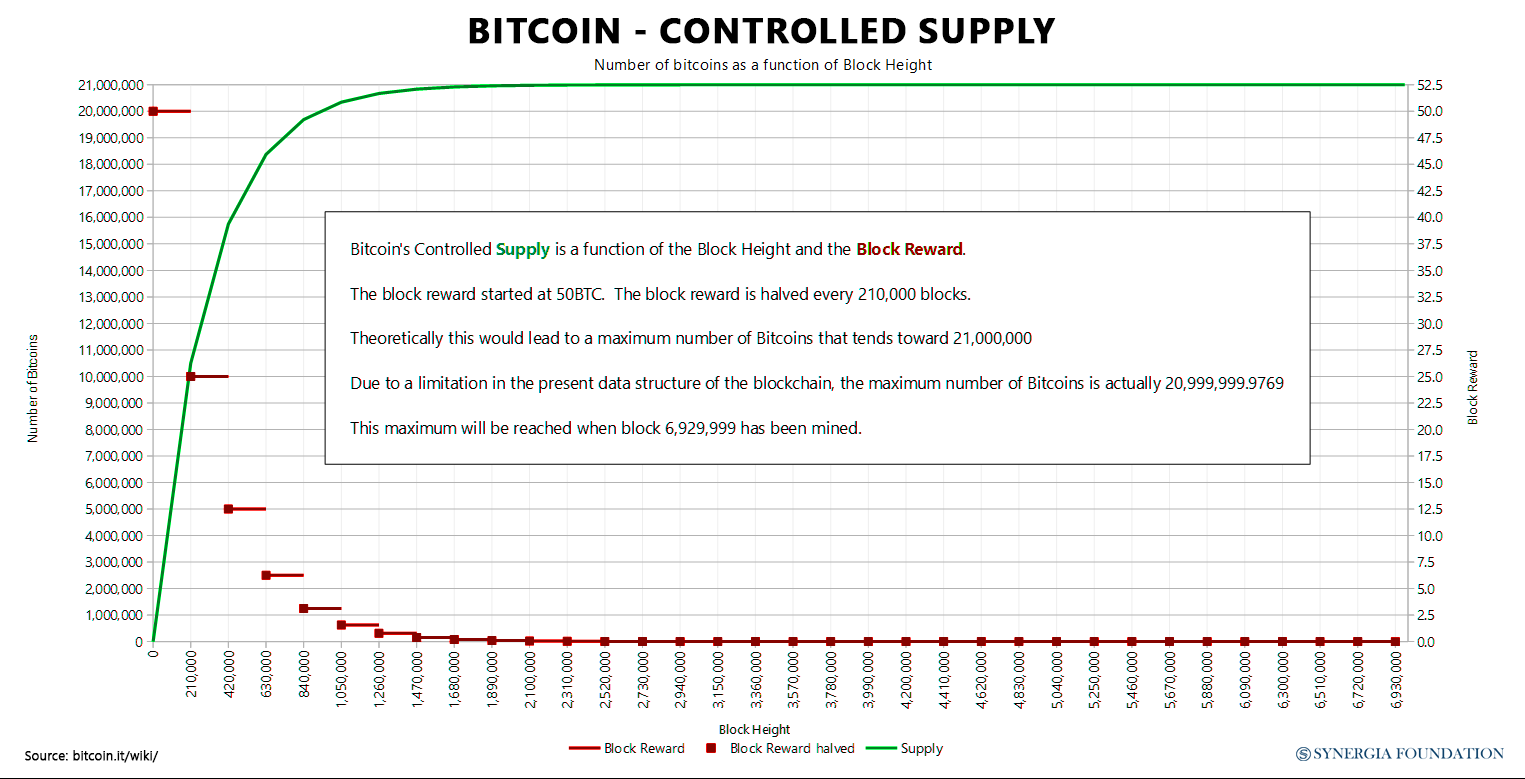
The hard limit set on bitcoin (at 21 million) allows for inflation to be controlled, as no one in any circumstance can introduce more money into the system. This also protects it from any possible political influence. Every four years, the number of Bitcoin introduced into the system is halved. This is by nature deflationary. Although the halving is deflationary, it also creates a viral loop. Bitcoin speculations have always correlated with halving, which has continuously increased its value.
Counterpoint
Although, in theory, bitcoin can act as a hedge against inflation, there are major monetary concerns that it does not address. Firstly, it does not have any fiscal backing like a centrally issued currency. If everyone decides that bitcoin has no value, its value will decline to zero. This is not true for centrally issued currencies. Secondly, central banks have inflation targets that they try to hit. Target inflation rates are important because they help the economy grow at a controlled rate. Also, for the most part, countries do not suffer from hyperinflation. It is uncertain how a cryptocurrency like bitcoin (or even a market of multiple cryptocurrencies) will ensure the hitting of inflation targets. Lastly, crypto advocates have missed out on the other roles that central banks play. They not only control inflation levels but also fight deflation and act as a lender of last resort. None of this has been addressed by bitcoin.
Assessment
- Theoretically, bitcoin can act as a hedge against inflation. If people continue to buy into its value, it may also be able to give higher returns to citizens than centrally issued money.
- Bitcoin has not addressed a range of issues currently handled by central authorities, like fighting deflation and acting as a lender of last resort.
- Bitcoin will most likely act as digital gold and not as a currency.







Comments