India China Blockchain Stack 1+1= 11
December 19, 2017 | Expert Insights
In our analog world, ‘soft power’ diplomacy challenged traditional ‘hard power’ assumptions where ‘geography is destiny’. In the digital world, topology, not geography, is destiny - and new assumptions have emerged around leveraging network effects, data diplomacy and the transformative importance of ‘software power’ - the power of ‘The Stack’.
Background
Blockchain is the world's leading software platform for digital assets. It is a decentralized and distributed digital ledger of cryptocurrency. It cannot be controlled by any single entity and it has no single point of failure. Blockchains are secure by design and are an example of a distributed computing system with high Byzantine fault tolerance. Decentralized consensus has therefore been achieved with a blockchain. The first blockchain was conceptualized in 2008 and was created by someone going by a possible pseudonym called Satoshi Nakamoto. Called the Bitcoin, it was implemented in 2009. The value of Bitcoins has exponentially increased in 2017. From being valued at $1,000 a year ago, recently Bitcoinshave been trading past $15,000.
Despite resistance to the Bitcoin, China seems to be navigating towards Blockchain. In June 2017, the People’s Bank of China opened its own new cryptocurrency research lab. PBoC, which is the central bank of China, has also made significant investments towards research in Blockchain. Additionally, in September 2017, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology launched a research facility called the Trusted Blockchain Open Lab. The facility was built to support the nation’s ongoing development of the technology.
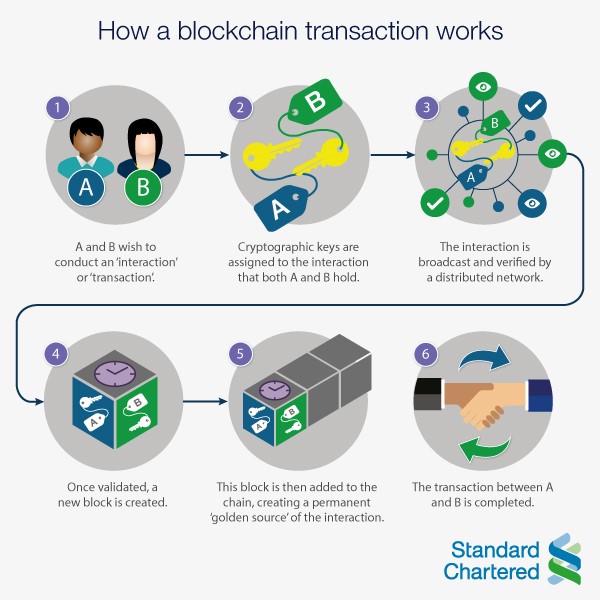
Analysis
Pindar Wong, Managing Director – Internet pioneer & Managing Director, VeriFi, Hong Kong spoke on the theme, ‘India China Blockchain Stack 1+1= 11’. He said that there is already a “silent war” on the individual. “It’s silent and it’s done at a scale of billions,” he said.
In particular he said that given environmental challenges at stake, there is now a common interest in provable sustainability as weather is being “weaponized” one way or the other. He said, “The weather does not see any borders; it is very similar to the internet.”
He also spoke about Belt and Road (One Belt One Road) and noted that it was designed to be the future of trade linking land, sea and air. However, there is a missing component – cyber. He noted that Hong Kong has provided an alternative for that. He along with his group have developed the Belt and Road blockchain. He spoke about security and the stability that it ushers. He said that it was imperative to police the blockchain. He said that the benefit of the Belt and Road blockchain is that it can be monitored noting, “We have to agree across 65 economies, that we are all going to watch one thing.” He proposed that India should build it but “with the cooperation of Hong Kong.” However, if it is to be built by Hong Kong, then the stakeholders need to make sure it is sustainable and green.
Speaking in particular about China and India he noted, “Once you understand we have a space now – cyberspace – which does not necessarily have to be scary, it can also be the same space where we can find trust.” This would require trust.
He said that the right question in the field is how this trust can be built and scaled. He said, “You can’t divorce your neighbors…and on the internet, everyone is your neighbor and every neighborhood is a bad neighborhood.” Thus, it is important to make sure “who we’re are dealing with.” He said that trust can be built by trusting Mathematics.
Assessment
Our assessment is that the Chinese government wants to foster international trade using block chain technology as a potentially useful, disintermediating tool for advancing its regional interest, especially in trade. We believe much work is being done to incorporate smart contacts, tokens and other aspects of block chain technology into supply-chain management systems that enhance information-sharing and efficiency. One such project is the BRICS “ E –Port network “ which is an electronic platform to process and monitor cross –border movement of merchandise and transportation vessels at a port level.








Comments