Fed holds off on rate hike
November 2, 2017 | Expert Insights

The Federal Reserve has voted to hold the interest rates steady between 1 and 1.25 percent. This is largely due to the fact the US economy has grown despite recent hurricanes that caused widespread damage to US states.
Background
The Federal Reserve System (also known as the Federal Reserve or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States. It was created on December 23, 1913. The main goal behind establishing the body was to create a central control of the monetary system that will prevent financial crises. In the event of a financial downturn, the Federal Reserve steps in to provide key aid.
Over the years, the Federal Reserve a played a key role in saving the American economy (and in turn the global economy) from imploding. It’s roles and responsibilities were expanded after the Great Depression, that caused a global meltdown. The timing of the Great Depression varied across nations; in most countries it started in 1929 and lasted until 1941. It resulted in international trade being reduced by 50% and unemployment rose.
A rise in the Fed funds rate will likely cause a ripple effect on the borrowing costs for consumers and businesses that want to access credit based on the U.S. dollar. Whenever the Federal Reserve increases the interest rates, the prime rate increases, and the credit card rates also increases among others. A hike in interest rates boosts the borrowing costs for the U.S. government and fuel an increase in the national debt.
In June 2017, the Federal Reserve stated that it would be hiking key interest rates by 0.25%. This was the second time in the year when the interest rates were hiked. The hike in the interest rates were reflective of the central bank's confidence in the US economy. After a two-day meeting on 14th June, the Federal Reserve’s Open Market Committee raised its benchmark interest rate by 25 basis points from a range of 1% to 1.25%.
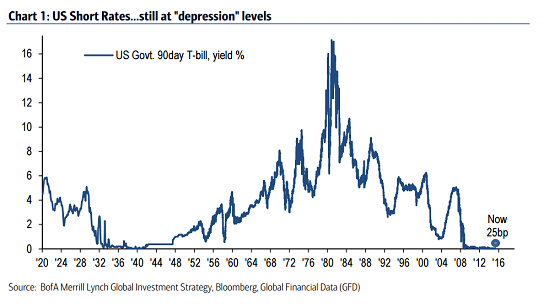
Analysis
The US economy expanded at an annual pace of 3% during the three months to the end of September. The growth rate is higher than what had been forecast by experts. In the previous quarter the US GDP grew at an annual pace of 3.1%. On a year-on-year basis, GDP was up 2.3% according to estimates. The economy has grown for eight straight years, one of the longest stretches in history. Unemployment is down to 4.2%, its lowest since 2001.
In light of strong economic growth in the US, the Federal Reserve policymakers announced that the body will hold a key interest rate steady at between 1 percent and 1.25 percent. The decision was announced a day before US President Donald Trump is expected to announce the next Federal Chair. There is only a slight chance that the current Federal Chair, Janet Yellen will be re-appointed. Markets expect the president to name Fed Governor Jerome "Jay" Powell to lead the central bank.
In a statement released by the Federal Reserve, spoke about how economic activity has sustained despite hurricanes adversely affecting US states like Texas and Florida. The statement noted, “In view of realized and expected labor market conditions and inflation, the Committee decided to maintain the target range for the federal funds rate at 1 to 1-1/4 percent. The stance of monetary policy remains accommodative, thereby supporting some further strengthening in labor market conditions and a sustained return to 2 percent inflation.”
Expert analysts are still unable to explain why inflation has hovered so low in the region – currently the inflation rates are 1.3%. The Federal Reserve has tried to pull it up to 2%. The statement also said, “In determining the timing and size of future adjustments to the target range for the federal funds rate, the Committee will assess realized and expected economic conditions relative to its objectives of maximum employment and 2 percent inflation.”
"There's no signal from today's meeting that there's any risk that December has been altered," said Michael Arone, chief investment strategist at State Street Global Advisors. "With the economy growing at roughly 3 percent, with unemployment at 4.2 percent, with very easy monetary conditions and a modest uptick in inflation expectations, everything leads me to believe that they'll be raising rates in December."
In addition to the rate hikes, the Fed in October began the process of gradually reducing its $4.5 trillion balance sheet.
Assessment
Our assessment is that the strong economic growth along with a drop in the unemployment rate in the US has provided confidence to investors and equity markets have risen as a result. The Fed already has raised rates twice this year as part of a program for a slow but steady normalization of monetary policy. This is the last meeting that will be held by the Federal Reserve before markets find out who the next Chair will be. Trump is widely expected to nominate Jerome Powell as her successor.








Comments