CONTROLLING CATASTROPHES WITH A CONSOLE
August 13, 2022 | Expert Insights

Experience is the application of practical skills to prove subjective outcomes of a circumstance. Hence, learning and experience go hand in hand when shaping a person's actions. This is the reason why education systems and policymakers are mandating the use of practical tools within the curriculum to ensure in-depth understanding.
However, in order to prepare citizens to face climate triggered calamities, it would be preferable to use virtual experience rather than the real thing.
Background
An upcoming method in educational spaces is the use of innovation and technology; since 2010, smart classes have become the norm. A decade later, it has become difficult to comprehend knowledge without the concept of "tech-ed".
Video games, often looked down upon as an addictive menace, are proving to have just the right kind of use. Interactive video games and AI simulations are now being used by top-level multilateral organisations like UNDRR (United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction) to launch a game called 'Stop Disasters'.
The concept is to expose gamers to a simulated environment prone to a natural calamity. If the user chooses Japan, they will have to make decisions and adjustments on an upcoming tsunami. The natural calamity could be a tornado if it is the United States. The game also has various difficulty levels. The main aim is to empower future policymakers with practical knowledge, although learnt virtually if they face such a situation of global distress.
A few years ago, Microsoft launched a global-level developers’ competition, where they posed an interesting narrative; to “imagine technology solving the world’s toughest problems”. A group of students from the Philippines, who had suffered the consequences of Typhoon Ketsana, developed a game called “Wildfire” aimed to tackle global health issues. The interference is based on gamers going around the city tackling global health issues "called the bad guys". The game is interesting because the gamers get inspiration points at each passing level. These inspiration points help the player gather volunteers and tackle global health issues together.
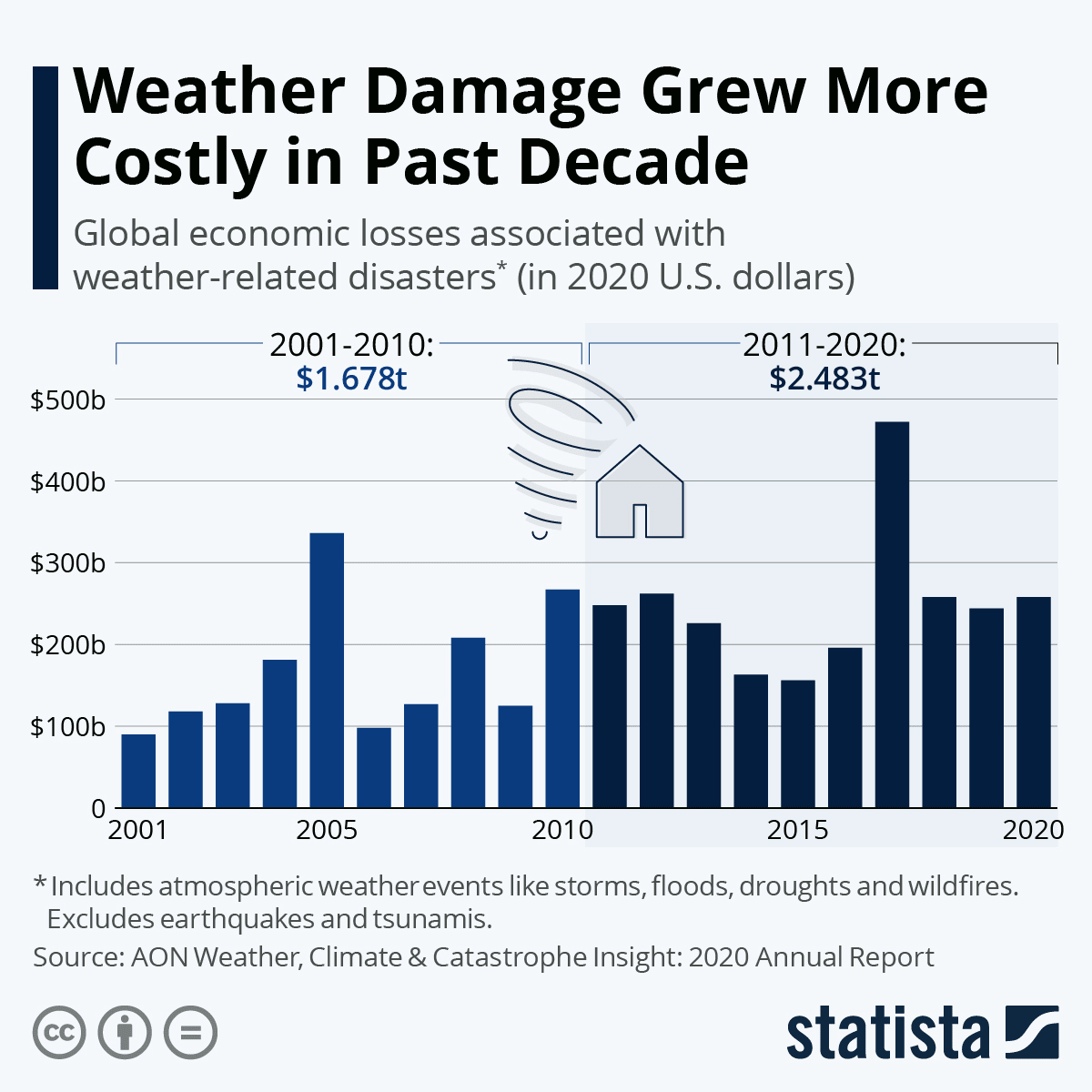
Analysis
A dynamic world needs innovative solutions which can be found only when we start to move away from traditional ways of perceiving knowledge and apply real-time remedies. The pros and cons of automation are two sides of the same coin. We need contemporary solutions to reverse the major consequences created by mankind due to its greed and uncaring attitude towards nature. To make amends, human beings must focus on preservation and effective recovery. With a wave of new ideas, one can optimistically presume that the world will find ingenious ways to deal with natural threats like pandemics, earthquakes, floods and fires.
Big issues like climate change can be averted with collective action and the idea can encompass other sectors like health, well-being, and development, as well as finding new cures. This is slowly shifting our perspectives from being on the receiving end of natural calamities to developing sustainable solutions.
In a world where there is scarcely a country that has not suffered a natural calamity, such an innovation would be very welcome. Caught off guard by cloud bursts, tsunamis, landslides, earthquakes etc., the authorities and citizens are left agonised and paralysed, unable to quickly respond and rescue their stricken compatriots. Such games that teach disaster risk management virtually could promote a greater sense of individual responsibility.
Assessment
- Governments would like individual citizens to share the blame for the environmental degradation causing these calamities and be a part of the solution. Research has proved that people conducted themselves more efficiently and responsibly during the second wave of the pandemic once it was clear that there was no other way to survive. Training them, even virtually, will strengthen the will to fight at the individual level.
- Knowledge engineering programmes for various natural disasters are an effective tool to train people on ways to escape and save themselves in the face of danger. One can call it the “innovative fire drill”.








Comments